Bug Bounty 101: The Best Courses to Get Started in 2025
August 13, 2025
17 min read
Bug bounty has been buzzing around the tech world for several years, and many companies are now paying ten times more than they used to. Bug bounty programs help organizations identify and fix bugs in their applications, attracting many hackers to participate and hunt for vulnerabilities. Bug bounty isn’t slowing down anytime soon, as companies continue to invest heavily in security. If you take a quick look at any active program, you’ll see that companies offer very competitive pay, ranging from $100 to $5000, depending on the severity of the reported bug.
In 2025, many startups and even governments are launching their own bug bounty programs instead of solely relying on their security teams. This approach is actually helping them identify bugs that their own team missed.
The best part of these programs is that you don’t need a degree to get started. If you’re willing to learn and understand how things actually work behind the web, then you’re good to go; all you need is a laptop and an internet connection.
In this article, we will review the top bug bounty courses you might want to enroll in 2025 to deepen your knowledge and increase your chances of earning rewards.
What is Bug Bounty program
You can think of a bug bounty program as a formal invitation for hackers to test a company’s products for potential vulnerabilities. Every company has its own program, which typically includes:
- Scope: the domain, sub-domains, or any other form of target description, listed by the company to test for vulnerabilities.
- Rules of engagement: something that could be defined as what kind of testing is allowed and what’s off-limits.
- Reward structure: tells you how much they pay for a valid bug.
Once you understand the policy, the real hunting begins. You can find your targets and active programs on platforms like HackerOne, Bugcrowd, Intigriti, YesWeHack, and some others. We will discuss these platforms in another post.
If you find a bug on any of these platforms, you are supposed to write a detailed report and generate a PoC (Proof of Concept) explaining the vulnerability and a methodology to reproduce it. Companies will then review your report and reward you based on its severity. If it’s a duplicate or doesn’t meet their criteria, it might get rejected, and that’s okay; we’ve all been there, and it’s all part of the learning process.
What hackers get paid for
Most bugs you discover will fall into a category called OWASP Top 10, and the severity of these bugs is also scaled based on this list. This list consists of almost every possible bug, starting from Broken access control to SSRF (Server Side Request Forgery). If you’ve found a low-impact bug, you can expect around $50-$100, but if you find something more critical, like full account takeover or access to sensitive data, then you could be looking at $1,000 to $5,000 or sometimes even more.
Imagine you’re about to make a trade, but instead of spending SHIB, Shiba Inu from your wallet, you’re selling BTC, which you don’t actually own. That’s like having unlimited money! This happened because of a missing validation check in the Coinbase API – the platform couldn’t verify that the crypto matched the user’s account. So someone could easily trick it into thinking they had Bitcoin when they didn’t and still make real trades.
This bug was reported by a security researcher, Tree of Alpha, in February 2022, earning a $250,000 bounty, which was the largest payout Coinbase has ever made.
.@Tree_of_Alpha you're awesome - a big thank you for working with our team
— Brian Armstrong (@brian_armstrong) February 11, 2022
love how the crypto community helps each other out!
If you’re curious about how such API bugs work, you should check out the courses listed below that focus mainly on API security.
Skills, Tools, & Platforms
Before getting started, we need to get our basics right. There are some prerequisites that you need to have before you take up any bug bounty course. You can start with:
- Understanding how HTTP requests work.
- Basics of networking, which includes TCP/IP and the OSI model.
- Working of the DNS (Domain Name System)
- Linux command line
Are these skills enough? No.
Coding and Scripting
One of the most common debates in bug bounty is whether you need to know programming. The answer is yes – having a basic understanding of at least one programming language is always helpful when searching for vulnerabilities. For example, many applications are built with HTML/CSS and, of course, JavaScript. So, before even learning how to exploit weaknesses, it’s important to understand how these are built.
Now, what about scripting? You’ll see this word a lot. Is it really necessary? Not when you’re just starting out. Scripting can be useful when you want to automate your daily tasks or build your own tools, but for beginners, most of what you need is already available. Finally, learning these languages would be your best choice.
- Web development: HTML/CSS, JavaScript
- Application development: Bash, Python, and GoLang
Hacking Tools
There are plenty of tools available, but trying to master every tool before targeting real systems can take years. Instead, you can start by quickly learning some of the most common tools used in application security or bug hunting.
A good way to start is by familiarizing yourself with Kali Linux. Learning its command line can save you a lot of time. It comes preloaded with most of the tools you’ll use in your daily tasks. Some of them are:
- Burpsuite
- OWASP ZAP
- Nmap
- Wireshark
- Metasploit
- Nuclei
- Httpx

Practice platforms to use
There are a few platforms where you can practice all the attacks in OWASP TOP 10 with different case scenarios. These platforms will help you simulate attacks that occur in the real world. Here are a few platforms that can assist you,
HackTheBox (HTB): a platform that helps you simulate attacks and find vulnerabilities. It is a CTF-style training platform where you can practice attacks related to different domains, including web.
TryHackMe (THM): Similar to HTB, THM is another platform where you find vulnerable rooms recreating real-world attack scenarios. These rooms include web as one of their categories.
Damn Vulnerable Web Application: DVWA is a vulnerable application that’s built on PHP/MariaDB. You can’t find this application online like HTB and THM. You are supposed to build your own lab using the Kali terminal. If you are a beginner, you might find it difficult to set it up, but once you do, it’s really fun and exciting when you start attacking. It contains most of the OWASP TOP 10 vulnerabilities.
bWAPP: Buggy Web Application is another vulnerable web application similar to DVWA. This one is unique and more interactive compared to DVWA. You can set it up on a Windows machine and also on your Kali Linux.
Recommended Reading
How to Detect CVEs Using Nmap Vulnerability Scan Scripts
Top Free Bug Bounty Courses
There are several excellent bug bounty courses available completely free of charge. Here are some of the best options to help you get started.
1. Portswigger Web Security Academy
PortSwigger Academy is designed by the same people who developed Burp Suite. They offer courses for beginners who are new to application security and are looking to learn things in a practical way and controlled environments. In my opinion, this course is always at the top of the list when searching for bug bounty courses, as it contains detailed hands-on labs for every single vulnerability that you might come across when you start hunting.
Where to find it
You can find this course on PortSwigger’s official website by navigating to the academy tab.
Link : PortSwigger Web Security Academy
What to expect
This course categorizes attacks into two types: client-side and server-side. Mastering each lab can help you cover most of the basics in security. To start, you can focus directly on their featured modules: SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), CSRF, and XXE.
With over 190 interactive labs, completing at least 7 labs a day will help you finish the entire course in a month. After finishing the courses, you are no longer a beginner and ready to target real-world scenarios, but don’t expect to find all the vulnerabilities you practice in labs on actual targets. Most people assume that, especially since some lab examples are basic, while real-world targets are much more complex.
2. Hacker101 by HackerOne
HackerOne, recognized as the leading bug bounty platform, also provides a course on application security called Hacker101. The course is straightforward and includes hands-on labs that demonstrate how real-world bugs work.
Where to find them
Head straight to the official Hacker101 website.
Link: Hacker101 by HackerOne
What to expect
This course consists of video lectures, and the labs are designed in CTF-style (Capture The Flag) to simulate real-world attack scenarios. Solving these challenges earns you points, making it feel more like a game than a traditional course. Once you accumulate enough CTF points, you can unlock private programs on HackerOne, which most regular hunters cannot access. You can complete this course if you finish at least 1-2 labs each day.
3. OWASP API Security Top 10 and Beyond
The two courses we have covered so far mainly focus on traditional web application security topics such as forms, sessions, cookies, and the usual OWASP TOP 10 bugs. However, this course is different; unlike the other two, OWASP API introduces you to a new category called the OWASP API Top 10 vulnerabilities.
Where to find it
You can check out this course on the official APIsec University website.
Link: OWASP API Security Top 10 and Beyond!
What to expect
This course features a video series taught by Corey Ball, focusing entirely on API security testing. I wouldn’t recommend this course for beginners right away because APIs are somewhat advanced topics; even if you understand how APIs work, testing them isn’t as simple as it seems. One of the best examples of API security issues is the Coinbase vulnerability we just examined.
In this course, Corey explains how APIs are designed and where they often fail. He demonstrates how to exploit common vulnerabilities in APIs, such as Broken Object Level Authorization, Broken Authentication, and mass assignment, using various tools.
This is one of the best free courses focused solely on API security, and the ideal time to complete it is about 10 hours.
4. API Penetration Testing
This one is again from the APIsec university. This course picks up where the OWASP API TOP 10 and Beyond leaves off. Again, this isn’t for beginners. If you’re already familiar with basic API security concepts and want to level up, this is the perfect next step.
Where to find it
Also hosted on APIsec University’s site. Like all their courses, it’s free.
Link: API Penetration Testing
What to expect
This course is made for people who want to go beyond the basics. In this course, you’ll set up a lab with live instructions. After that, you’ll learn how to discover and map out APIs before starting the attack, essentially doing recon. This course also teaches you how to craft your payloads, which I believe is the best way to learn how to break things. After finishing this course, you can manually test APIs without relying on tools.
The duration of this course is about 6–8 hours. I recommend taking your time to try things out instead of rushing through the entire series.
5. Android Application Security
This course is highly underrated and was created by MobileHackingLab. There aren’t many quality courses available in this field, so if you’re not just focused on web security and want to explore something beyond web, then this is a good choice.
Where to find it
Navigate to the courses tab on the official page of MobileHackingLab’s website, and you’ll find it there.
Link: MobileHackingLab
What to expect
If you’re new to Android security, this is an ideal starting point. It is beginner-friendly, but they do expect you to have some basic knowledge of Android application development.
In this course, you’ll work with a vulnerable Android app. Unlike web security, Android application security introduces you to new tools like MobSF, Frida, Apktool, and others. When learning Android application security, we usually assume you need a rooted device or a physical Android phone, but for this course, you don’t need either. It’s compatible with Android emulators and test environments. This course also prepares you for one of their certification exams called CAPT (Certified Android Penetration Tester), which is a paid credential.
Request Your Free 14-Day Trial
Submit a request to try Netlas free for 14 days with full access to all features.
Paid Bug Bounty Courses
Below is a list of excellent paid courses worth considering, depending on your goals and experience.
6. HTB Certified Bug Bounty Hunter
CBBH is an industry-standard certificate offered by HackTheBox, which is a CTF platform. This course is for beginners and for those who are looking to invest in quality courses, provided they have some basic knowledge of application security.

When to invest
First, let’s understand the pricing structure of this course. The certification exam costs $210. But wait, the course content is much cheaper, and you can unlock it using a subscription plan. There are two subscription plans available to unlock this course:
Student Subscription - $7/month Platinum Subscription - $84 for 2 months, gives you 2000 cubes, which is enough to unlock the whole path.
The certificate cost is quite expensive for beginners, but unlocking the course content can be worth it. If you are a beginner, now is the right time to unlock the course and start learning. You can purchase the exam voucher later, once you’re confident with the material.
What makes it worth it
The course content is good, starting from the basics of web applications and then moving to advanced topics of application security like XSS, SQLi, and SSRF, covering most of the attacks from the OWASP Top 10. You’ll need approximately 3-5 weeks to complete the course and prepare for the exam. As this is an industry-standard certificate, you can always use this as a credential when applying for internships or jobs.
Link: HTB Certified Bug Bounty Hunter
7. Burp Suite Certified Practitioner
Burp Suite Certified Practitioner (BSCP) can be considered the OSCP for web. This certificate, offered by Portswigger, consists of a 4-hour practical exam, which includes two vulnerable systems with a total of 12 challenges that you are supposed to hack and exploit. You must solve at least 9 out of 12 challenges to pass the exam.

When to invest
Looking at the exam structure, it’s obvious that this isn’t an entry-level cert. The right time to purchase this certificate is after you complete most of the Web Security Academy labs, especially the Practitioner and Expert level ones.
The BSCP exam costs around $125 for a single attempt. However, to attempt the exam, you must have a licensed version of Burp Suite Pro, which costs $449 per year. Since it is pricey, I suggest you purchase the exam only once you’re confident in your skills.
What makes it worth it
Passing the BSCP exam is worth it because this certification prepares you to hunt the most secure targets in the real world. This can also be used as a qualification if you are applying for any jobs related to pentesting or application security, which increases your chances of getting hired. The BSCP certificate is valid for five years from the date of issue.
Link: Burp Suite Certified Practitioner
8. eLearnSecurity Web Application Penetration Tester
This certificate is perfect for those seeking a more structured alternative to CBBH. It covers all aspects of application pentesting, from recon and enumeration to exploitation.

When to invest
The pricing for this course is quite high and confusing. The eWPT Exam Voucher costs $599 and includes 3 months of INE Premium access. After those 3 months, you’ll be automatically enrolled in a 9-month extension for $350 unless you decide to cancel.
If you’re planning to take this certificate, I would suggest you study the course content accordingly and try the exam within the first 3 months to avoid extensions.
What makes it worth it
The course content is highly structured around practical black-box penetration testing, and the quality of the labs is excellent. Some older reviews mention that the content is outdated and that exams can be unpredictable. However, with recent updates, those who have passed the exam say that this certification still provides value, especially for demonstrating strong skills in advanced web application pentesting. It’s also an excellent way to build confidence before pursuing bug bounty targets or preparing for larger certifications like OSCP.
Link: eLearnSecurity Web Application Penetration Tester
9. Intro to Bug Bounty Hunting and Web Application Hacking
There are a lot of bug bounty courses for beginners out there, but this one is among my favorites because it’s designed by Nahamsec. Nahamsec has been part of the bug bounty community for years, not just as a top hacker but also as a community builder, streamer, and speaker. He’s someone many beginners admire and aspire to become like.
When to invest
I recommend purchasing this course during a Udemy sale, as you can get it for as low as $15. The regular price of the course is around $80. Once you buy it, it’s yours for life.
What makes it worth it
This course offers 11.5 hours of video content organized into different topics, ranging from basic to advanced levels. Even if you’re not yet fully comfortable with the basics, you can still take this course because it is very beginner-friendly. The course also introduces various methodologies to help you reach your target, and I must say, NahamSec’s bug bounty strategies never fail. They are straightforward, clear, and consistently effective. Although the course lasts 11.5 hours, I recommend spending at least two weeks to fully absorb the material.
Link: Intro to Bug Bounty Hunting and Web Application Hacking
10. TCM Practical Bug Bounty
TCM Security has partnered with Intigrity to build this course. This course is designed to give you an actual workflow for web hacking, demonstrating exactly how you are supposed to deal with your targets in the real world.
When to invest
This is another budget-friendly option, designed for beginners. It costs around $29/month, which I feel is quite reasonable, and it gives you access to their complete course content.
What makes it worth it
This course clearly explains how web apps are built, covering the most common web architectures, including both client-side and server-side components of web applications. You’ll also learn about some of the most common bugs like IDOR, Open Redirects, XSS, Broken Access Control, and more.
After completing this course, you’ll be able to pick up a program, identify bugs, and create a comprehensive report. This course includes approximately 7 hours of video content; you can finish it in a week or two, depending on your schedule.
Link: TCM Practical Bug Bounty
Choosing the Right Course
With so many courses available, choosing the right one can be tough, so let’s narrow it down by your skill level, preferred format, and budget.
Based on skill level
Beginners: Suppose you have no idea where to start, but you’ve come here with the thought of learning bug bounty. In that case, I suggest you start with PortSwigger Web Security Academy, followed by Hacker101 and the TCM Practical Bug Bounty course. These are self-paced and cover most of the basics, though you may not be familiar with the prerequisites already.
Intermediate: Considering you have a basic understanding of how the web works, you can start with courses like HTB Certified Bug Bounty Hunter (CBBH), OWASP API Top 10 and Beyond, or even Intro to Bug Bounty Hunting and Web Application Hacking by Nahamsec. These are great for intermediaries who don’t want to start everything from scratch.
Advanced: People who are already in the job and understand how things work can go with Burp Suite Certified Practitioner, API Penetration Testing, or eLearnSecurity Web Application Penetration Tester (eWPT).
Based on Format
I see people are very particular about how they prefer to learn, so categorizing these courses by their format might actually help you pick the right one.
Interactive labs & challenges: Courses like PortSwigger Academy, Hacker101, and HackTheBox CBBH are very practical. They’re great if you prefer learning things by trying out stuff practically rather than reading through PDFs.
Video-focused learning: Now, if you’re someone who learns by watching videos, courses like NahamSec’s Practical Bug Bounty, APISec University, and TCM Security’s Practical Bug Bounty training offer video content with clear and practical breakdowns.
Self-hosted or emulator-based: These courses are best for people who want to get their hands dirty by setting up their lab. I suggest going for API Penetration Testing, Android Application Security, or eWPT.
Based on the Budget
| Course | Cost | Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| TCM Practical Bug Bounty | $29/month | Start here if you’re new to bug bounty; this is great for fundamentals. |
| Intro to Bug Bounty (Nahamsec) | $15 (on sale) | Grab it during a Udemy sale. |
| HTB Certified Bug Bounty Hunter (CBBH) | $210 | Complete the course before attempting the exam; use the student plan if possible |
| BSCP (Burp Suite Certified Practitioner) | $125 + Burp Pro ($449/year) | Finish PortSwigger Academy labs first and only attempt when you’re confident. |
| eWPT (eLearnSecurity Web PenTesting) | $599 + $350 extension (optional) | Plan to finish in the first 3 months to avoid extra charges on extension. |
Tips for Beginners
Practice alongside theory
As we discussed earlier in the “practice platforms to use” part of this article, I recommend setting up your lab environment and practicing alongside the theory and videos. Getting hands-on experience will enhance your understanding of how attacks work in the real world.
For example, take XSS; simply reading about the types of XSS won’t teach you how to test for these attacks on your target. Instead, try attacking the labs you’ve set up – spotting the requests and injecting payloads will give you a much clearer understanding.
Join communities
Joining security communities is one of the best ways to meet new people. You might find a mentor or like-minded individuals working on the same course, certification, or project as you. Some Discord channels I suggest joining:
HackTheBox: A community with over 318,042 members gives you access to hacking challenges, labs, and the HTB Academy.
TryHackMe: It is focused on beginner-friendly cybersecurity learning you can chat with others about walkthroughs, challenges, and CTFs
DavidBombal: Everything about networks and cybersecurity can be discussed here; this server is led by David Bombal, a famous YouTuber.
Nahamsec: - A community over 35,711 members actively discussing bug bounty, recon, and offensive security.
Take notes and revisit
Write down everything you see, hear, and learn, like commands, tools, bugs, or techniques and procedures, which will help you recap the topics. Notion and Obsidian are digital notebooks, which are a great choice for taking notes. Revisit these notes regularly to track your progress.
Automation is a key to success
By 2025, everything is automated. Nearly every task in cybersecurity can be automated if you have strong scripting skills. Whether it’s scanning targets or exploiting vulnerabilities, automation helps save time. Mastering scripting tools like Bash and Python or automating workflows with platforms like Burp Suite (using extensions or macros), Nmap (using NSE scripts), can decrease your manual testing workload.
Here’s an example: you can write a one-liner Bash command to automatically fetch URLs using waybackurls, scan them with gau, and then pipe the output into tools like gf for filtering potential parameters, which can save a lot of time during reconnaissance.
One-liner Command:
echo "target.com" | waybackurls | tee wayback.txt && gau target.com | tee gau.txt && cat wayback.txt gau.txt | sort -u | gf xss It’s okay if you don’t understand the command right now; many beginners feel the same. It will all make sense once you start learning it step by step.
Recommended Reading
Domain Recon: Must-Know Tools for Security Professionals
Real-World Success Stories
I. Santiago Lopez – $9,000 Bug on Twitter via HackerOne
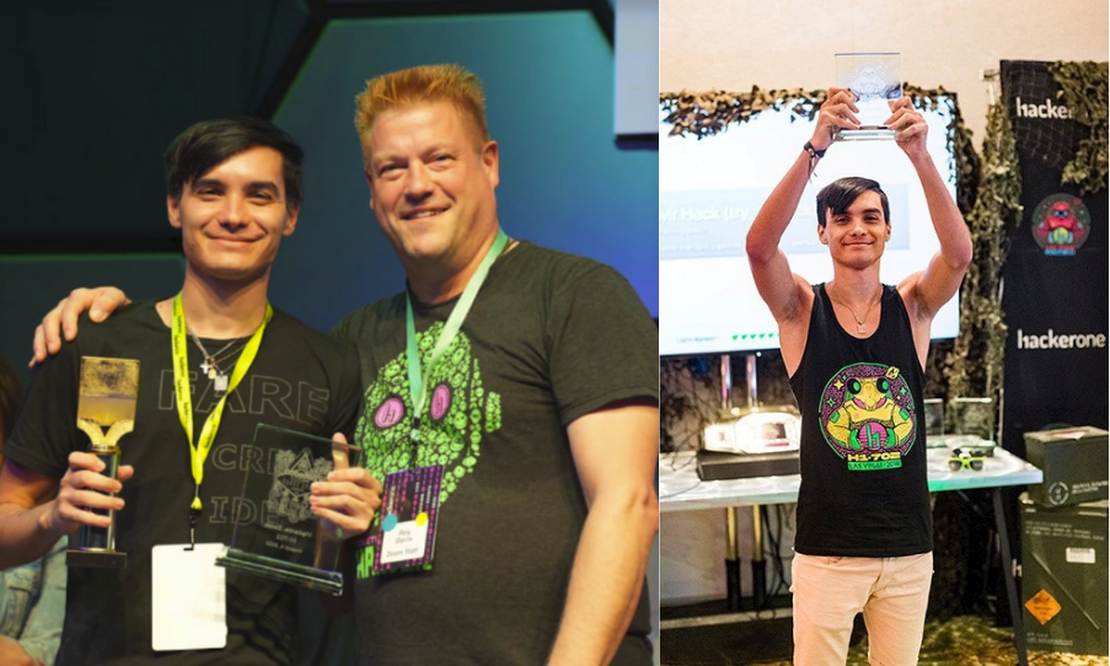

Santiago Lopez, also known as @try_to_hack, was one of the first hackers on HackerOne to earn over a million dollars. At just 19 years old, he managed to hack into Twitter and change users’ email settings without their knowledge. His scripting skills enabled him to create malicious requests, which he injected and later used to take over accounts. This vulnerability is called CSRF or Cross-Site Request Forgery, which exploits users’ authenticated sessions. He earned around $9,000 for this single bug. This example shows how much someone can make from bug bounties.
Santiago rewarded himself with cars, computers, and a beach house on a private estate. You could be the next one in a few years if you start now. In an interview, he mentioned that he generally spends around 6-7 hours hacking, mostly in the evenings, which has helped him reach his current level.
II. Frans Rosen
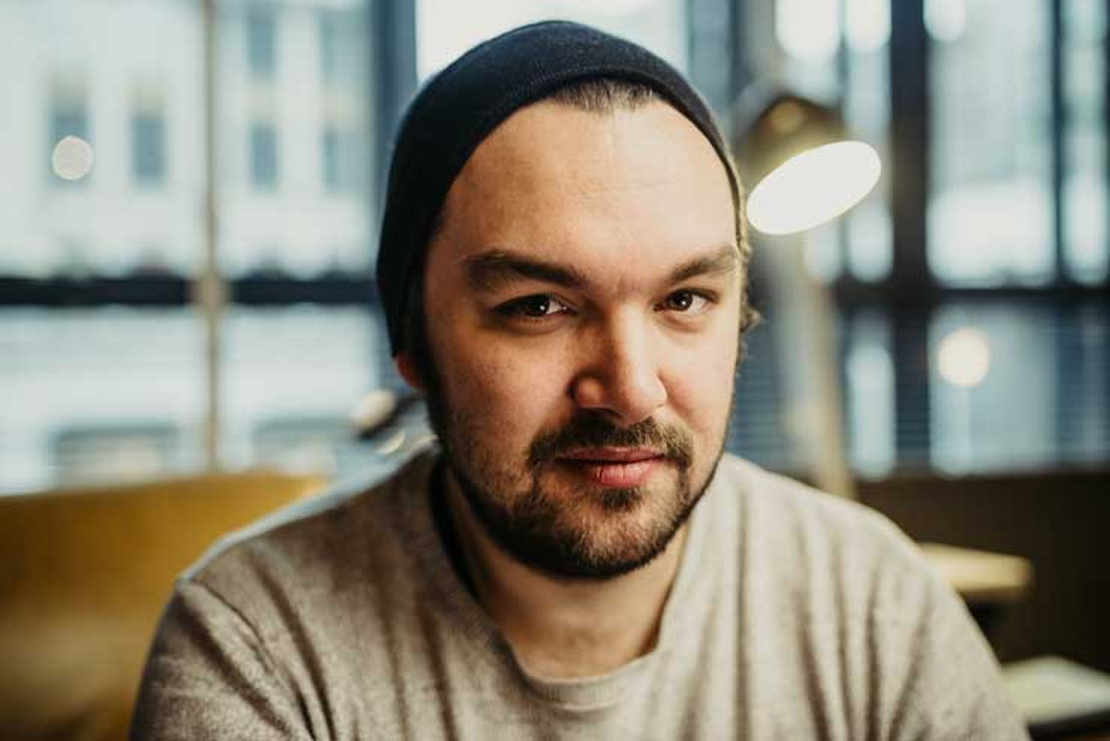

Frans Rosen is a security researcher with over $1.5 million in total bug bounty rewards. With more than 876 vulnerabilities reported on HackerOne, he is considered one of the top researchers. Rosen is an experienced hunter. He once reported a CORS misconfiguration on a SaaS platform that allowed an attacker to read sensitive data, including internal API responses across origins, which is a very critical issue and could lead to account takeovers. Most of his findings are kept confidential for some reason, but we understand that he is earning a lot by hunting bugs in applications.
What’s Next
Sign up on platforms
We have looked at almost everything in detail, starting from what a bug is, how it is reported, and how much you get paid. It’s time to sign up on platforms like HackerOne, Bugcrowd, Intigriti, and start hunting. Delaying anything from here on will only put you one step behind others. There are many targets out there on those platforms waiting for you, so let’s not waste time and get to work.
Start with Small Scopes
For beginners, choosing a target can be very confusing and might lead to selecting the wrong one. So let’s start with a small scope rather than focusing on the top programs. After picking a target with a small scope, spend some time understanding their policies before jumping straight into attacking. It’s better to report one valid low-severity bug than to chase a critical one and burn out. In a later post in this series, we will also cover how to pick your first target.
Build Your Portfolio
A good portfolio speaks louder than your resume. The portfolios that you are going to create on HackerOne and Bugcrowd will help you stand out from the crowd someday. HackerOne portfolios prove that you actually have the industry exposure that all the HR professionals are looking for. You can also start writing security blogs and publish them online on Medium, which will help you build your online presence.
Keep Learning
The technologies you see today might not even exist tomorrow. As a hacker, you’ll often come across new technologies in your targets every day. That’s why continuous learning helps you stay updated. Here’s a tip I follow to stay updated: turn on notifications for the Medium app, and every time someone posts a blog, you get notified. Sure, some titles are kind of clickbait, but there’s still something valuable to learn. I read at least 10 blogs a day, and honestly, it’s one of the best habits that helps me hunt smarter.
Final Thoughts
Should You Learn Bug Bounty? Absolutely, you should!!! Now that we are in 2025, bug bounty is getting way more popular. Many people are just getting started, including professional developers switching their careers to become security researchers. But it’s never too late; this is the right time to start learning and step into the field.
Bug bounty is more than just code and exploits; it’s a mindset, a thrill, and a journey of endless learning. Stay tuned, because in the next blog of this series, we’ll guide you through picking your first target and mastering recon, step by step!

I can show you how deep the Internet really goes
Discover exposed assets, infrastructure links, and threat surfaces across the global Internet.
Related Posts

June 19, 2025
Nmap Cheat Sheet: Top 10 Scan Techiques

June 14, 2025
Domain Recon: Must-Know Tools for Security Professionals

June 16, 2025
Google Dorking in Cybersecurity: Techniques for OSINT & Pentesting

July 25, 2025
The Pyramid of Pain: Beyond the Basics

September 13, 2024
7 Tools for Web Penetration Testing

August 8, 2025
I, Robot + NIST AI RMF = Complete Guide on Preventing Robot Rebellion